An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.This law is often called "the law of inertia".![]()
SECOND LAW OF MOTION
Acceleration is produced when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass (of the object being accelerated) the greater the amount of force needed (to accelerate the object).
Everyone knows that heavier objects require more force to move the same distance as lighter objects.
The Second Law gives us an exact relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. It can be expressed as a mathematical equation:
F=MA
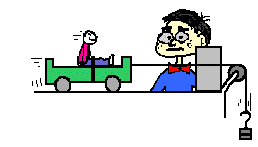
This is an example of how Newton's Second Law works:![]()
Mike's car, which weighs 1,000 kg, is out of gas. Mike is trying to push the car to a gas station, and he makes the car go 0.05 m/s/s. Using Newton's Second Law, you can compute how much force Mike is applying to the car.
![]()
Answer = 50 newtons
THIRD LAW OF MOTION
For every action there is an equal and opposite re-action.
This means that for every force there is a reaction force that is equal in size, but opposite in direction. That is to say that whenever an object pushes another object it gets pushed back in the opposite direction equally hard.
The rocket's action is to push down on the ground with the force of its powerful engines, and the reaction is that the ground pushes the rocket upwards with an equal force.
|


No comments:
Post a Comment